Articular Cartilage Regeneration
What is Articular Cartilage?
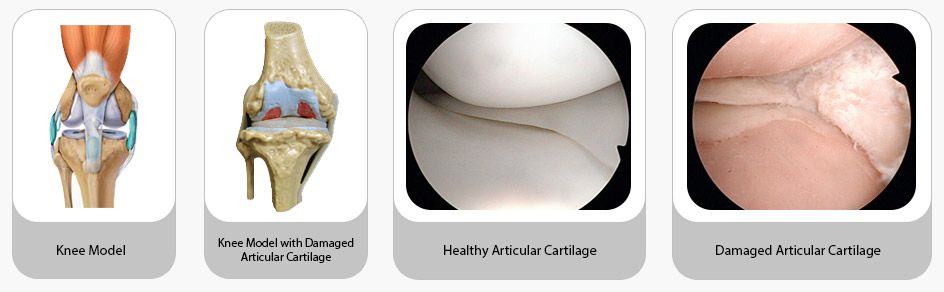
Articular cartilage is the smooth, white tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint, such as the knee, ankle and wrist. The articular cartilage functions to dissipate load, provide lubrication and allows the bones to glide over each other with very little friction during joint movement.
What are the common causes of cartilage injuries?
Cartilage injuries can occur either at the tibio-femoral joint or the patella-femoral joint. These can be caused by trauma, wear and tear or other underlying causes.
Tibio-femoral Joint:
- Malalignment (varus or valgus deformity)
- Instability
- Meniscus-related
Patella-femoral Joint:
- Patella maltracking
- Plica syndrome
What are the available solutions for cartilage injuries?
Current available solutions for cartilage injuries are pain management, reparative surgery or total knee replacement. The benchmark to treat cartilage injuries in the USA is microfracture, a marrow stimulation technique where tiny fractures are made at the subchondral bone, inducing bone marrow stem cells to home to the damaged site, stimulating repair. This technique is simple and cost effective but only fibrocartilage is regenerated. As fibrocartilage is not native to the knee joint, it breaks down in 2 years.
Our research in articular cartilage regeneration with stem cells has shown to regenerate hyaline cartilage while conventional treatments have only been able to regenerate fibrocartilage.
Why cartilage injuries will not heal like other tissues?
Partial and full thickness cartilage injuries have a limited ability to heal naturally. This is because the cartilage is lack of blood supply and hence, limited access to the body’s own existing stem cells.
What are the advantages of Stem Cell Therapy over Knee Replacement in cartilage injury or osteoarthritis?
Total knee replacement surgery (TKR) is an excellent remedy for patients suffering from advanced osteoarthritis of the knee. The surgery has been shown to significantly improve joint mobility and daily functions. Patients will enjoy permanent relief from pain, enabling them to stop relying on the long-term use of pain killers. A well-performed knee replacement surgery can last for 15 to 20 years, but a revision may be required thereafter. Nevertheless, TKR patients may not be able to run, jump or lead very active lifestyles after the procedure.
Stem cell therapy on the other hand, provides an innovative solution to cartilage injury and osteoarthritis. It has a wide appeal because it offers preservation of your own knee anatomy by enabling cartilage regeneration. It is a better option for some patients who still intend to go back to playing sports or leading an active lifestyle.
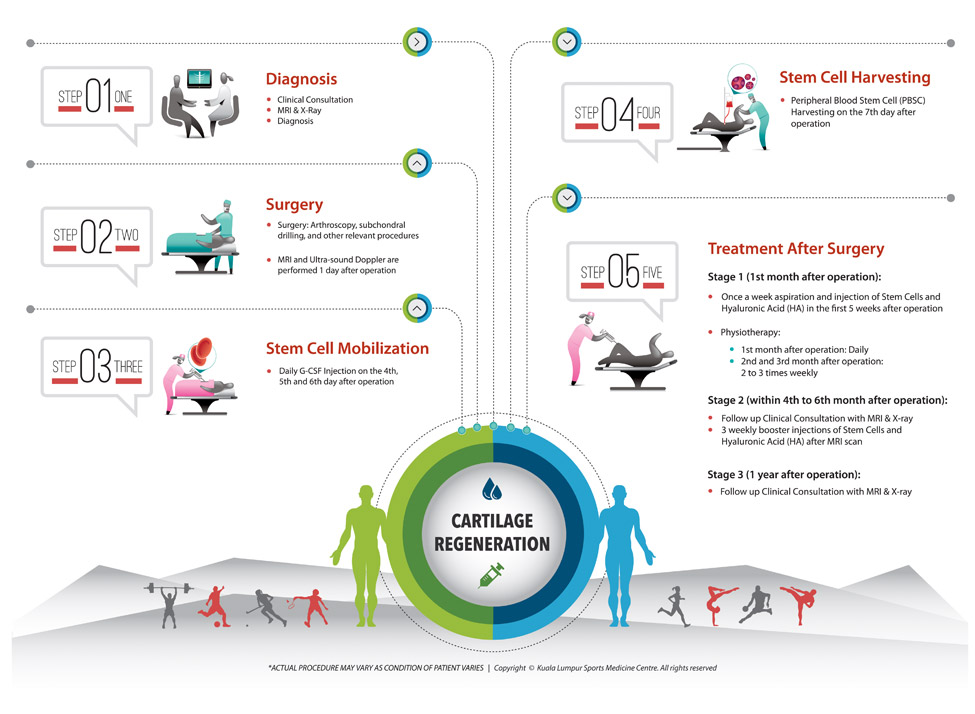
Our Procedures
What are KLSMC’s stem cells treatment procedures?
The step by step procedures of our stem cell treatment is outline in the diagram below.